Do you struggle with circulation in your legs and feet, often finding your leg falling asleep or your toes getting cold quickly? There are many reasons why this may be happening, and one of them could be due to Niacin deficiency. This is everything you need to know about this powerful vitamin and how to get more of it in your daily diet.
What is Niacin?

Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. It is one of the eight B vitamins and is available in two primary chemical forms: nicotinic acid and niacinamide. The main function of niacin in the body is to synthesize coenzymes that are involved in over 400 biochemical reactions. In particular, those related to energy metabolism.
Symptoms of Niacin Deficiency

Niacin deficiency is also known as pellagra. It can lead to a range of symptoms that can affect various systems in the body. Some common symptoms of niacin deficiency include:
- Skin Issues: Dermatitis, which is characterized by inflamed, scaly skin, especially in sun-exposed areas, is one of the hallmark symptoms of niacin deficiency. The skin may become thick, rough, and develop a darkened, rough texture.
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain are common. These symptoms can also lead to poor appetite and weight loss.
- Mental Health Concerns: These include symptoms like irritability, anxiety, depression, memory loss, and cognitive impairment. In severe cases, psychosis and delirium may develop.
- Fatigue and Weakness: General fatigue, weakness, and decreased physical endurance. This can affect overall energy levels and daily activities.
- Burning Sensations: Known as Peripheral neuropathy, some individuals may experience a sensation of burning, tingling, or numbness in the hands and feet.
- Digestive System Problems: Different from regular gastrointestinal symptoms, these include things like mouth sores, a bright red tongue, and inflammation of the mouth and throat.
- Photosensitivity: Niacin deficiency can make individuals more sensitive to sunlight, leading to an increased risk of sunburn and skin damage upon exposure.
How Niacin Improves Circulation in the Legs and Feet

Niacina plays a crucial role in supporting healthy circulation in the legs and feet through its vasodilatory effects. Vasodilation refers to the widening of blood vessels, which leads to increased blood flow, decreased blood pressure, and improved circulation throughout the body. This includes the extremities.
Prostaglandin Production
Niacin triggers the production of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that have vasodilatory properties. Specifically, niacin stimulates the production of prostaglandin D2, prostaglandin E1, and prostaglandin E2. These prostaglandins act on the smooth muscles of blood vessels, causing them to relax and widen. As a result, blood flow is enhanced, ensuring that an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients reaches the tissues in the legs and feet.
Increased Blood Flow
This vasodilatory effect of niacin leads to a significant increase in blood flow to the lower extremities. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions that may compromise circulation in the legs and feet, such as peripheral artery disease (PAD) or diabetes. By promoting vasodilation, niacin helps mitigate the narrowing of blood vessels and the consequent reduction in blood flow, which can lead to improved sensation, reduced discomfort, and better overall function in the lower extremities.
Lowering Cholesterol
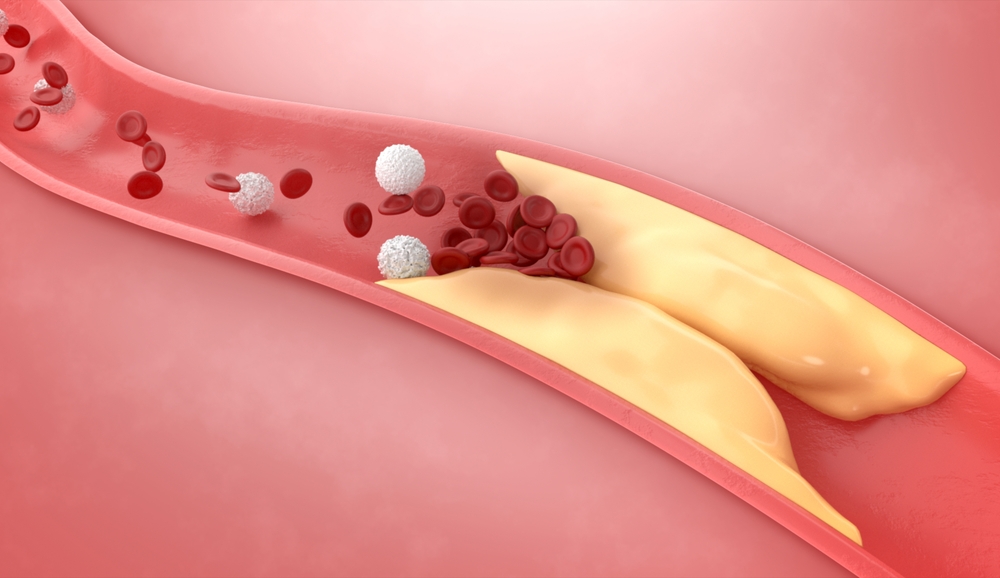
Niacin’s ability to lower LDL cholesterol levels and triglycerides can indirectly contribute to improved circulation. High levels of these substances can contribute to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits in the arterial walls, leading to restricted blood flow. By lowering these lipid levels, niacin helps reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, thereby promoting healthier circulation in the legs and feet.
Read More: Popular Vitamins and Supplements Linked to Liver Failure
Supporting Endothelial Function
Niacin also supports endothelial function, which is essential for maintaining the health and flexibility of blood vessels. Endothelial dysfunction can impair blood vessel function, leading to reduced vasodilation and compromised circulation. Niacin’s role in supporting endothelial health contributes to the maintenance of optimal blood vessel function, which is vital for promoting efficient circulation in the lower extremities.
Other Benefits of Niacin

In addition to enhancing circulation, niacin offers a range of other health benefits. As already mentioned, it may help to lower cholesterol and reduce triglycerides. It may also boost brain function and improve skin health. Niacin plays an important role in converting food into energy by aiding essential enzymes and is involved in cell signaling, DNA repair, and acting as an antioxidant.
Foods High in Niacin
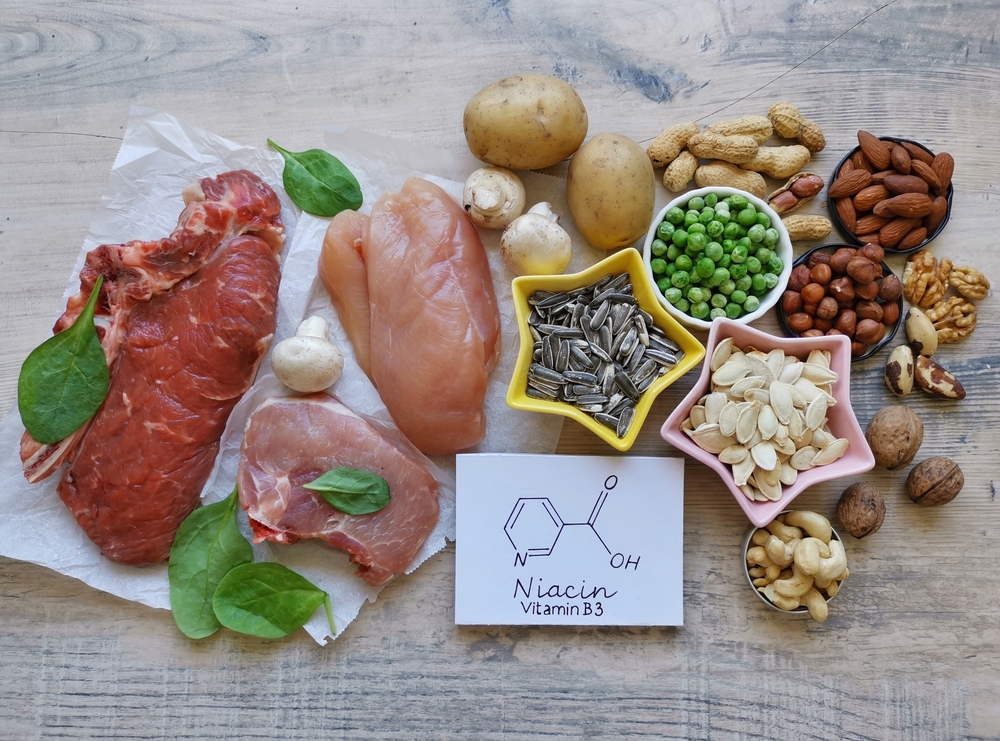

Thankfully, getting more Niacin in your diet is not difficult. This includes vegetarians and vegans. Some of the foods high in niacin include:
- Grilled chicken breast: 3 ounces provides 64% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Roasted turkey breast: 3 ounces provides 63% of the DV
- Cooked brown rice: 1 cup provides 33% of the DV
- Dry roasted peanuts: 1 ounce provides 26% of the DV
- Medium baked potato: 14% of the DV
How to Increase Your Niacin Intake

To increase niacin intake, it is simple: eat more foods high in the vitamin. This includes meat, fish, nuts, and legumes. Additionally, some foods are fortified with niacin, such as some breakfast cereals. Getting niacin from food sources is always safe, with no fear of overconsuming or any side effects. Taking it in supplement form, however, can lead to various side effects. These will generally only be recommended for specific medical conditions or deficiencies, and the directive will come straight from your healthcare provider.
The Bottom Line

Niacin stands out as a valuable vitamin that not only supports overall health but also aids in improving circulation, particularly in the legs and feet. By understanding the role of niacin, incorporating niacin-rich foods into your diet, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals when considering supplementation, you can use this vitamin to improve your health.
Read More: Why Vitamin D Deficiency is More Complex Than Just Getting Sunlight or Popping a Pill
